CBSE Class 12 Biology Syllabus 2025-26: The Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) has released the Biology syllabus for Class 12 Science stream for the academic year 2025-26. This official syllabus PDF includes the complete course structure, chapters, and topics that students need to study. It also explains the exam pattern and assessment details. Biology is an important subject for Science students, especially those preparing for exams like NEET and CUET. A good understanding of Biology not only helps in scoring well in board exams but also plays a key role in clearing competitive entrance tests. This syllabus will help students plan their preparation in a clear and focused way. The CBSE Class 12 Biology syllabus is designed to:
- Strengthen students' understanding of core concepts in Biology.
- Encourage the use of theoretical knowledge in real-life scenarios.
- Develop the skills needed for higher studies in fields like medicine, biotechnology, and microbiology.
- Forms the foundation for entrance exams like NEET, CUET, and other medical or life science-based tests..
CBSE 12th Biology Syllabus 2025-26 Download PDF
The CBSE Class 12 Biology Syllabus is designed to help students clearly understand all the important topics in the subject. It supports strong preparation for both board exams and competitive entrance exams like NEET and CUET. To get good marks, students should go through the syllabus carefully and study regularly. Below is the direct link to download the CBSE Class 12 Biology Syllabus PDF.
CBSE 12th Biology Syllabus 2025-26 Download PDF
The CBSE Class 12 Biology Syllabus for 2025-26 helps students understand concepts clearly, develop analytical thinking, and apply their knowledge to real-life situations. To score well, students should begin their preparation early, study consistently, and focus on understanding the topics instead of just memorising them. Below, you can find the full syllabus with unit-wise marks and other important details.
Unit I: Reproduction
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Flower structure: development of male and female gametophytes; pollination - types, agencies and examples; out breeding devices; pollen-pistil interaction; double fertilization; post fertilization events - development of endosperm and embryo, development of seed and formation of fruit; special modes- apomixis, parthenocarpy, polyembryony; Significance of seed dispersal and fruit formation.
- Human Reproduction: Male and female reproductive systems; microscopic anatomy of testis and ovary; gametogenesis -spermatogenesis and oogenesis; menstrual cycle; fertilisation, embryo development up to blastocyst formation, implantation; pregnancy and placenta formation (elementary idea); parturition (elementary idea); lactation (elementary idea).
- Reproductive Health: Need for reproductive health and prevention of Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs); birth control - need and methods, contraception and medical termination of pregnancy (MTP); amniocentesis; infertility and assisted reproductive technologies - IVF, ZIFT, GIFT (elementary idea for general awareness).
Unit II: Genetics and Evolution
- Principles of Inheritance and Variation Heredity and variation: Mendelian inheritance; deviations from Mendelism – incomplete dominance, co-dominance, multiple alleles and inheritance of blood groups, pleiotropy; elementary idea of polygenic inheritance; chromosome theory of inheritance; chromosomes and genes; Sex determination - in humans, birds and honey bee; linkage and crossing over; sax linked inheritance - haemophilia, colour blindness; Mendelian disorders in humans - thalassemia; chromosomal disorders in humans; Down's syndrome, Turner's and Klinefelter's syndromes.
- Molecular Basis of Inheritance: Search for genetic material and DNA as genetic material; Structure of DNA and RNA; DNA packaging; DNA replication; Central Dogma; transcription, genetic code, translation; gene expression and regulation - lac operon; Genome, Human and rice genome projects; DNA fingerprinting.
- Evolution: Origin of life; biological evolution and evidences for biological evolution (paleontology, comparative anatomy, embryology and molecular evidences); Darwin's contribution, modern synthetic theory of evolution; mechanism of evolution - variation (mutation and recombination) and natural selection with examples, types of natural selection; Gene flow and genetic drift; Hardy- Weinberg's principle; adaptive radiation; human evolution.
Unit III: Biology and Human Welfare
- Human Health and Diseases: Pathogens; parasites causing human diseases (malaria, dengue, chikungunya, filariasis, ascariasis, typhoid, pneumonia, common cold, amoebiasis, ring worm) and their control; Basic concepts of immunology - vaccines; cancer, HIV and AIDS; Adolescence - drug and alcohol abuse.
- Microbes in Human Welfare: Microbes in food processing, industrial production, sewage treatment, energy generation and microbes as bio-control agents and bio-fertilizers. Antibiotics; production and judicious use.
Unit IV: Biotechnology and its Applications
- Biotechnology - Principles and Processes: Genetic Engineering (Recombinant DNA Technology).
- Biotechnology and its Applications: Application of biotechnology in health and agriculture: Human insulin and vaccine production, stem cell technology, gene therapy; genetically modified organisms - Bt crops; transgenic animals; biosafety issues, biopiracy and patents.
Unit V: Ecology and Environment
- Organisms and Populations: Population interactions - mutualism, competition, predation, parasitism; population attributes- growth, birth rate and death rate, age distribution.
- Ecosystems: Patterns, components; productivity and decomposition; energy flow; pyramids of number, biomass, energy.
- Biodiversity and its Conservation: Biodiversity-Concept, patterns, importance; loss of biodiversity; biodiversity conservation; hotspots, endangered organisms, extinction, Red Data Book, Sacred Groves, biosphere reserves, national parks, wildlife, sanctuaries and Ramsar sites.
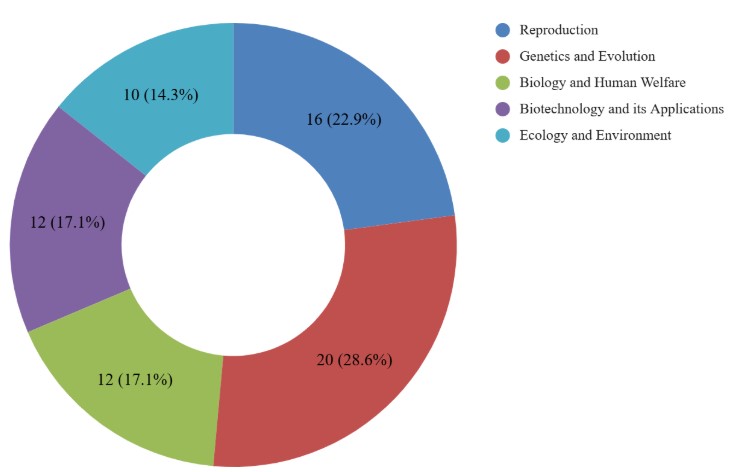
CBSE Class 12 Biology Unit-wise Weightage
The CBSE Class 12 Biology syllabus is divided into different units, and each unit carries specific marks in the board exam. Knowing the unit-wise weightage helps students prepare in a smart and focused way. It highlights which chapters are more important and need more attention. For example, Genetics & Evolution and Reproduction are among the units with higher marks. Below is the detailed unit-wise marks distribution to help you plan your studies better for the final exam.
| Unit No. | Unit Name | Marks |
| I | Reproduction | 16 |
| II | Genetics and Evolution | 20 |
| III | Biology and Human Welfare | 12 |
| IV | Biotechnology and its Applications | 12 |
| V | Ecology and Environment | 10 |
| Total | 70 | |
| Practical | 30 |
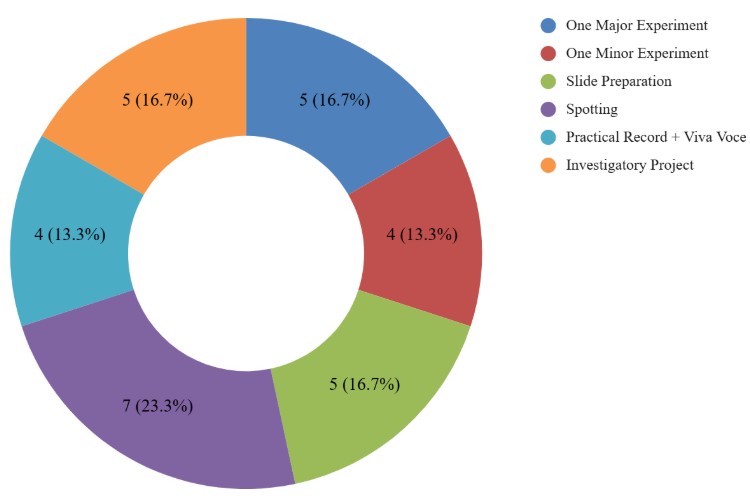
Practical is further divided into five components, i.e., Experiments, Slide Preparation, Spotting, Practical record, Investigatory Project, and Viva, whose breakup is given below:
| Component | Marks |
| One Major Experiment | 5 |
| One Minor Experiment | 4 |
| Slide Preparation | 5 |
| Spotting | 7 |
| Practical Record + Viva Voce | 4 |
| Investigatory Project | 5 |
| Total | 30 |
Tips for Covering the CBSE Class 12 Biology Syllabus Effectively
- Understand the Biology Syllabus Thoroughly: Before you begin your preparation, carefully go through the entire Biology Syllabus and marking scheme provided by CBSE. This helps you focus on the most important topics.
- Create a Study Plan: Divide the Biology Syllabus into manageable sections and create a realistic study plan. Allocate time for each section based on its difficulty level and your comfort.
- Use NCERT Books: CBSE recommends NCERT textbooks for exam preparation, as most of the questions are based on these books. Read the chapters thoroughly and practice the questions at the end.
- Create Revision Notes: Create concise revision notes with essential formulas, concepts, and important points for quick last-minute review.
- Solve Sample Papers and Previous Years Papers: CBSE releases sample question papers every year to help students get familiar with the exam pattern. Solve as many sample papers and previous year's question papers as possible. Also, solve chapter-wise board questions to gain a strong command over each chapter.
- Focus on Practical: In subjects like Biology, ensure you spend sufficient time in the lab and understand the experiments thoroughly.
- Revise Regularly: Keep revising the concepts regularly, and make sure to cover all the important topics at least two months before the exams.


