CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Syllabus 2025-26: The Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) has released the Chemistry syllabus for Class 12 Science stream for the academic year 2025-26. This official syllabus PDF includes the complete course structure, chapters, and topics that students need to study. It also provides information about the exam pattern and assessment guidelines. Chemistry is a key subject for Science stream students, especially for those preparing for competitive exams like JEE, NEET, CUET, and NDA. A strong understanding of Chemistry not only helps in scoring well in board exams but also plays an important role in cracking national-level entrance tests. This syllabus will help students plan their studies in a focused and effective way. The CBSE Class 12 Chemistry syllabus is carefully designed to:
- Help students understand basic concepts, principles, and laws of Chemistry.
- Encourage the practical application of theoretical knowledge.
- Build a solid academic foundation in the subject.
- Support preparation for various competitive exams.
CBSE 12th Chemistry Syllabus 2025-26 Download PDF
The CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Syllabus is designed to give students a clear understanding of all important concepts in the subject. It helps them prepare well for both board exams and competitive entrance tests. To score well, students should study the syllabus thoroughly and put in regular effort. Below is the direct link to download the CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Syllabus PDF.
CBSE 12th Chemistry Syllabus 2025-26 Download PDF
The CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Syllabus for 2025-26 is designed to help students clearly understand concepts, think analytically, and solve real-life problems. To score good marks, students should start their preparation early, study regularly, and focus on understanding the topics instead of just memorizing them. Below, you can check the complete syllabus with unit-wise marks and other important details.
Unit I: Solutions
- Types of solutions, expression of concentration of solutions of solids in liquids, solubility of gases in liquids, solid solutions, Raoult’s law, colligative properties - relative lowering of vapor pressure, elevation of boiling point, depression of freezing point, osmotic pressure, determination of molecular masses using colligative properties, abnormal molecular mass, Van't Hoff factor
Unit II: Electrochemistry
- Redox reactions, EMF of a cell, standard electrode potential, Nernst equation and its application to chemical cells, Relation between Gibbs energy change and EMF of a cell, conductance in electrolytic solutions, specific and molar conductivity, variations of conductivity with concentration, Kohlrausch's Law, electrolysis and law of electrolysis (elementary idea), dry cell-electrolytic cells and Galvanic cells, lead accumulator, fuel cells, corrosion.
Unit III: Chemical Kinetics
- Rate of a reaction (Average and instantaneous), factors affecting rate of reaction: concentration, temperature, catalyst; order and molecularity of a reaction, rate law and specific rate constant, integrated rate equations and half-life (only for zero and first order 10 reactions), concept of collision theory (elementary idea, no mathematical treatment), activation energy, Arrhenius equation.
Unit IV: d and f Block Elements
- General introduction, electronic configuration, occurrence and characteristics of transition metals, general trends in properties of the first row transition metals – metallic character, ionization enthalpy, oxidation states, ionic radii, colour, catalytic property, magnetic properties, interstitial compounds, alloy formation, preparation and properties of K2Cr2O7 and KMnO4. Lanthanides - Electronic configuration, oxidation states, chemical reactivity and lanthanide contraction and its consequences. Actinides - Electronic configuration, oxidation states and comparison with lanthanides
Unit V: Coordination Compounds
- Coordination compounds - Introduction, ligands, coordination number, colour, magnetic properties and shapes, IUPAC nomenclature of mononuclear coordination compounds. Bonding, Werner's theory, VBT, and CFT; structure and stereoisomerism, importance of coordination compounds (in qualitative analysis, extraction of metals and biological system).
Unit VI: Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
- Haloalkanes: Nomenclature, nature of C–X bond, physical and chemical properties, optical rotation mechanism of substitution reactions.
- Haloarenes: Nature of C–X bond, substitution reactions (Directive influence of halogen in monosubstituted compounds only). Uses and environmental effects of - dichloromethane, trichloromethane, tetrachloromethane, iodoform, freons, DDT.
Unit VII: Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
- Alcohols: Nomenclature, methods of preparation, physical and chemical properties (of primary alcohols only), identification of primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols, mechanism of dehydration, uses with special reference to methanol and ethanol.
- Phenols: Nomenclature, methods of preparation, physical and chemical properties, acidic nature of phenol, electrophilic substitution reactions, uses of phenols.
- Ethers: Nomenclature, methods of preparation, physical and chemical properties, uses
Unit VIII: Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
- Aldehydes and Ketones: Nomenclature, nature of carbonyl group, methods of preparation, physical and chemical properties, mechanism of nucleophilic addition, reactivity of alpha hydrogen in aldehydes, uses.
- Carboxylic Acids: Nomenclature, acidic nature, methods of preparation, physical and chemical properties; uses.
Unit IX: Amines
- Amines: Nomenclature, classification, structure, methods of preparation, physical and chemical properties, uses, identification of primary, secondary and tertiary amines.
- Diazonium salts: Preparation, chemical reactions and importance in synthetic organic chemistry.
Unit X: Biomolecules
- Carbohydrates - Classification (aldoses and ketoses), monosaccahrides (glucose and fructose), D-L configuration oligosaccharides (sucrose, lactose, maltose), polysaccharides (starch, cellulose, glycogen); Importance of carbohydrates.
- Proteins -Elementary idea of - amino acids, peptide bond, polypeptides, proteins, structure of proteins - primary, secondary, tertiary structure and quaternary structures (qualitative idea only), denaturation of proteins; enzymes. Hormones - Elementary idea excluding structure.
- Vitamins - Classification and functions.
- Nucleic Acids: DNA and RNA.
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Unit-wise Weightage
The CBSE Class 12 Chemistry syllabus is divided into different units, and each unit has a set number of marks in the board exam. Knowing the unit-wise weightage helps students plan their preparation better. It shows which chapters are more important and need extra focus. For example, the units on Electrochemistry and Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids have higher weightage in the exam. Below, you can find the detailed unit-wise marks distribution to help you prepare smartly for the final exam.
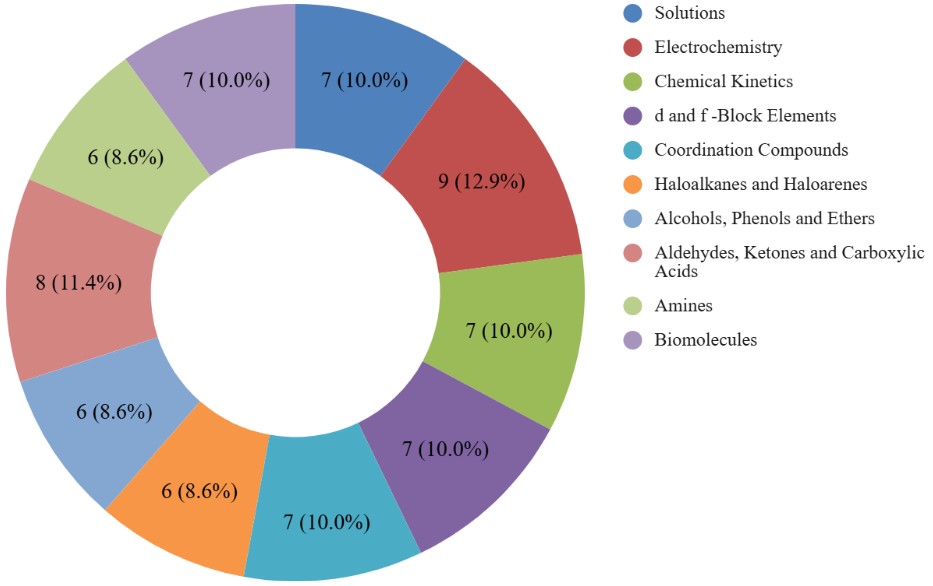
| Unit No. | Unit Name | Marks |
| I | Solutions | 7 |
| II | Electrochemistry | 9 |
| III | Chemical Kinetics | 7 |
| IV | d and f -Block Elements | 7 |
| V | Coordination Compounds | 7 |
| VI | Haloalkanes and Haloarenes | 6 |
| VII | Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers | 6 |
| VIII | Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids | 8 |
| XI | Amines | 6 |
| X | Biomolecules | 7 |
| Total | 70 | |
| Practical | 30 |
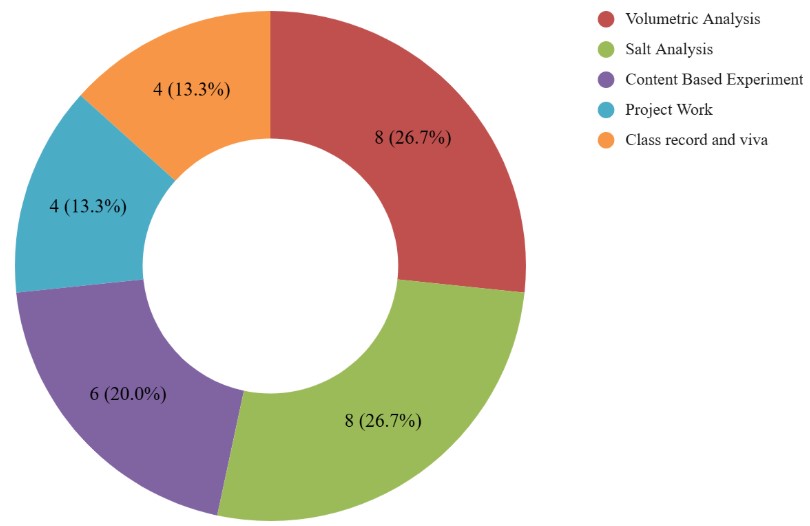
Practical is further divided into five components, i.e., Experiments, Practical record, Activity, Investigatory Project, and Viva, whose breakup is given below:
| Component | Marks |
| Volumetric Analysis | 8 |
| Salt Analysis | 8 |
| Content Based Experiment | 6 |
| Project Work | 4 |
| Class record and viva | 4 |
| Total | 30 |
Tips for Covering the CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Syllabus Effectively
- Understand the Chemistry Syllabus Thoroughly: Before you begin your preparation, carefully go through the entire Chemistry Syllabus and marking scheme provided by CBSE. This helps you focus on the most important topics.
- Create a Study Plan: Divide the Chemistry Syllabus into manageable sections and create a realistic study plan. Allocate time for each section based on its difficulty level and your comfort.
- Use NCERT Books: CBSE recommends NCERT textbooks for exam preparation, as most of the questions are based on these books. Read the chapters thoroughly and practice the questions at the end.
- Create Revision Notes: Create concise revision notes with essential formulas, concepts, and important points for quick last-minute review.
- Solve Sample Papers and Previous Years Papers: CBSE releases sample question papers every year to help students get familiar with the exam pattern. Solve as many sample papers and previous year's question papers as possible. Also, solve chapter-wise board questions to gain a strong command over each chapter.
- Focus on Practical Subjects: For subjects with practical components, ensure you spend sufficient time in the lab and understand the experiments thoroughly.
- Revise Regularly: Keep revising the concepts regularly, and make sure to cover all the important topics at least two months before the exams.


