CBSE Class 12 Physics Syllabus 2025-26: The Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) has released the Class 12 Physics Syllabus for Science stream for the 2025-26 academic year. This Class 12th Physics Syllabus PDF outlines the course structure, chapters, and topics that students will need to study in the subject. Additionally, it provides details about the exam pattern and assessment criteria. Physics is one of the core subjects for students in the Science stream, and plays a crucial role in preparing for competitive exams like JEE, NEET, CUET, and NDA. A strong foundation in this subject not only ensures excellent board results but also boosts preparation for competitive exams. This article will be helpful for students to understand the curriculum and plan their studies accordingly. The CBSE Class 12 Physics Syllabus is designed to:
- Help students understand the fundamental principles, laws, and theories of physics.
- Encourage students to apply theoretical concepts in solving real-life problems and scientific situations.
- Provide a strong academic foundation.
- Prepare students for national-level competitive exams.
CBSE 12th Physics Syllabus 2025-26 Download PDF
The CBSE Class 12 Physics Syllabus is designed to give students a clear and complete understanding of Physics. It helps them get ready for higher studies and competitive exams. A deep understanding of the Physics Syllabus, combined with consistent effort, is essential for achieving success in the assessments. Below, students can get the direct link to download the CBSE Class 12 Physics Syllabus PDF.
CBSE 12th Physics Syllabus 2025-26 Download PDF
The CBSE Class 12 Physics Syllabus for 2025-26 helps students understand concepts clearly, improve analytical thinking, and develop real-life problem-solving skills. To score well, students should start studying early, stay regular, and try to understand the topics instead of just rote memorising them. Below, you can see the full syllabus with unit-wise marks and other useful details.
Unit I: Electrostatics
- Electric Charges and Fields: Electric charges, Conservation of charge, Coulomb's law-force between two-point charges, forces between multiple charges; superposition principle and continuous charge distribution. Electric field, electric field due to a point charge, electric field lines, electric dipole, electric field due to a dipole, torque on a dipole in uniform electric field. Electric flux, statement of Gauss's theorem and its applications to find field due to infinitely long straight wire, uniformly charged infinite plane sheet and uniformly charged thin spherical shell (field inside and outside).
- Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance: Electric potential, potential difference, electric potential due to a point charge, a dipole and a system of charges; equipotential surfaces, electrical potential energy of a system of two-point charges and of an electric dipole in an electrostatic field. Conductors and insulators, free charges and bound charges inside a conductor. Dielectrics and electric polarisation, capacitors and capacitance, combination of capacitors in series and in parallel, capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor with and without dielectric medium between the plates, energy stored in a capacitor (no derivation, formulae only).
Unit II: Current Electricity
- Current Electricity: Electric current, flow of electric charges in a metallic conductor, drift velocity, mobility and their relation with electric current; Ohm's law, V-I characteristics (linear and non-linear), electrical energy and power, electrical resistivity and conductivity, temperature dependence of resistance, Internal resistance of a cell, potential difference and emf of a cell, combination of cells in series and in parallel, Kirchhoff's rules, Wheatstone bridge.
Unit III: Magnetic Effects of Current and Magnetism
- Moving Charges and Magnetism: Concept of magnetic field, Oersted's experiment. Biot-Savart law and its application to current-carrying circular loop. Ampere's law and its applications to an infinitely long straight wire. Straight solenoid (only qualitative treatment), force on a moving charge in uniform magnetic and electric fields. Force on a current-carrying conductor in a uniform magnetic field, force between two parallel current-carrying conductors-definition of ampere, torque experienced by a current loop in uniform magnetic field; Current loop as a magnetic dipole and its magnetic dipole moment, moving coil galvanometer- its current sensitivity and conversion to ammeter and voltmeter.
- Magnetism and Matter: Bar magnet, bar magnet as an equivalent solenoid (qualitative treatment only), magnetic field intensity due to a magnetic dipole (bar magnet) along its axis and perpendicular to its axis (qualitative treatment only), torque on a magnetic dipole (bar magnet) in a uniform magnetic field (qualitative treatment only), magnetic field lines. Magnetic properties of materials- Para-, dia- and ferro–magnetic substances with examples, Magnetisation of materials, effect of temperature on magnetic properties.
Unit IV: Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents
- Electromagnetic Induction: Electromagnetic induction; Faraday's laws, induced EMF and current; Lenz's Law, Self and mutual induction.
- Alternating Current: Alternating currents, peak and RMS value of alternating current/voltage; reactance and impedance; LCR series circuit (phasors only), resonance, power in AC circuits, power factor, wattless current. AC generator, Transformer.
Unit V: Electromagnetic waves
- Electromagnetic Waves: Basic idea of displacement current, Electromagnetic waves, their characteristics, their transverse nature (qualitative idea only). Electromagnetic spectrum (radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible, ultraviolet, X-rays, gamma rays) including elementary facts about their uses.
Unit VI: Optics
- Ray Optics and Optical Instruments:
Ray Optics: Reflection of light, spherical mirrors, mirror formula, refraction of light, total internal reflection and optical fibres, refraction at spherical surfaces, lenses, thin lens formula, lens maker’s formula, magnification, power of a lens, combination of thin lenses in contact, refraction of light through a prism.
Optical instruments: Microscopes and astronomical telescopes (reflecting and refracting) and their magnifying powers.
- Wave Optics: Wave front and Huygen’s principle, reflection and refraction of plane wave at a plane surface using wave fronts. Proof of laws of reflection and refraction using Huygen’s principle. Interference, Young's double slit experiment and expression for fringe width (No derivation, final expression only), coherent sources and sustained interference of light, diffraction due to a single slit, width of central maxima (qualitative treatment only).
Unit VII: Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
- Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter: Dual nature of radiation, Photoelectric effect, Hertz and Lenard's observations; Einstein's photoelectric equation-particle nature of light. Experimental study of photoelectric effect. Matter waves-wave nature of particles, de-Broglie relation.
Unit VIII: Atoms and Nuclei
- Atoms: Alpha-particle scattering experiment; Rutherford's model of atom; Bohr model of hydrogen atom, Expression for radius of nth possible orbit, velocity and energy of electron in nth orbit, hydrogen line spectra (qualitative treatment only).
- Nuclei: Composition and size of nucleus, nuclear force, Mass-energy relation, mass defect; binding energy per nucleon and its variation with mass number; nuclear fission, nuclear fusion.
Unit IX: Electronic Devices
- Semiconductor Electronics: Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits: Energy bands in conductors, semiconductors and insulators (qualitative ideas only). Intrinsic and extrinsic semiconductors- p and n type, p-n junction. Semiconductor diode - I-V characteristics in forward and reverse bias, application of junction diode -diode as a rectifier.
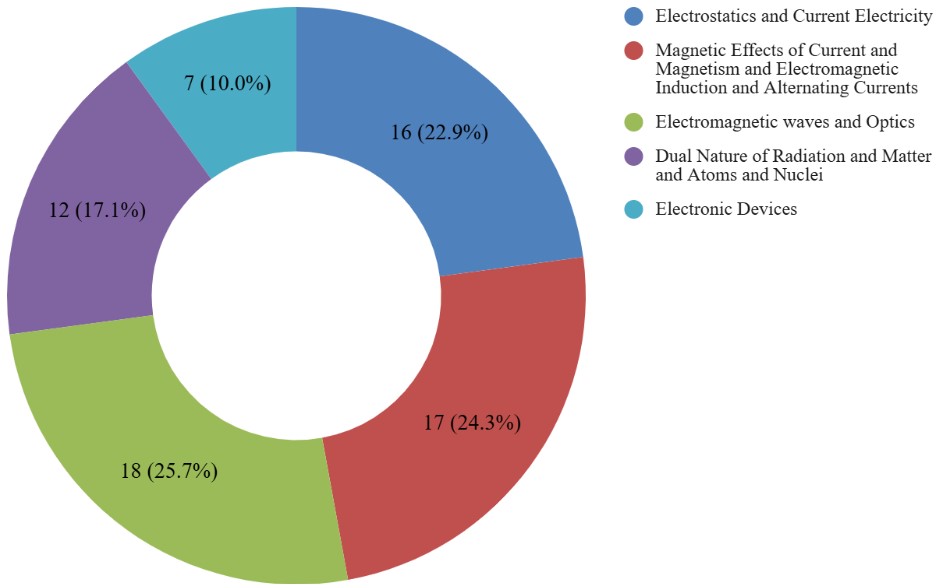
CBSE Class 12 Physics Unit-wise Weightage
The CBSE Class 12 Physics syllabus is divided into several units, each carrying a specific weightage in the board exam. Understanding the unit-wise weightage helps students prioritise their preparation. The combined units of Electromagnetic Waves and Optics have the highest weightage of 18 marks. Below, we are providing the CBSE 12th Physics Unit-wise weightage for your reference. This distribution helps students understand which topics need more attention to score well in the final exam.
| Unit No. | Unit Name | Marks |
| I | Electrostatics |
16 |
| II | Current Electricity | |
| III | Magnetic Effects of Current and Magnetism |
17 |
| IV | Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents | |
| V | Electromagnetic waves |
18 |
| VI | Optics | |
| VII | Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter |
12 |
| VIII | Atoms and Nuclei | |
| XI | Electronic Devices | 7 |
| Total | 70 | |
| Practical | 30 |
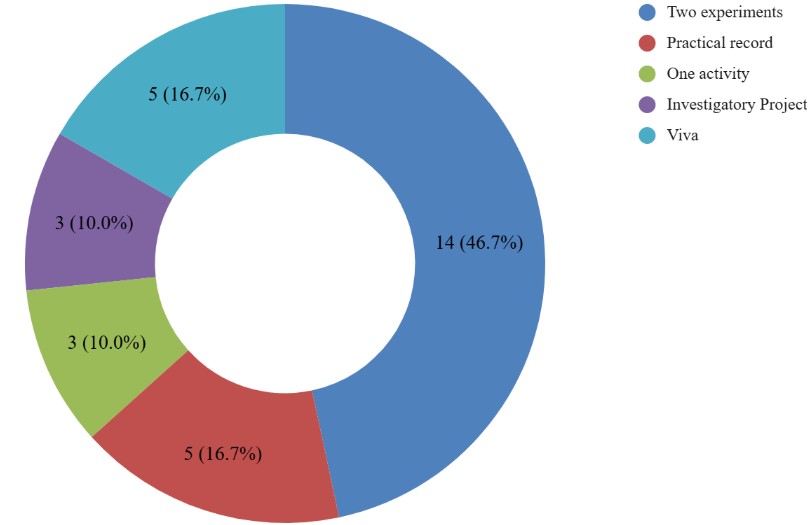
Practical is further divided into five components, i.e., Experiments, Practical record, Activity, Investigatory Project, and Viva, whose breakup is given below:
| Component | Marks |
| Two experiments | 14 |
| Practical record | 5 |
| One activity | 3 |
| Investigatory Project | 3 |
| Viva | 5 |
| Total | 30 |
Tips for Covering the CBSE Class 12 Physics Syllabus Effectively
- Understand the Physics Syllabus Thoroughly: Before you begin your preparation, carefully go through the entire Physics Syllabus and marking scheme provided by CBSE. This helps you focus on the most important topics.
- Create a Study Plan: Divide the Physics Syllabus into manageable sections and create a realistic study plan. Allocate time for each section based on its difficulty level and your comfort.
- Use NCERT Books: CBSE recommends NCERT textbooks for exam preparation, as most of the questions are based on these books. Read the chapters thoroughly and practice the questions at the end.
- Create Revision Notes: Create concise revision notes with essential formulas, concepts, and important points for quick last-minute review.
- Solve Sample Papers and Previous Years Papers: CBSE releases sample question papers every year to help students get familiar with the exam pattern. Solve as many sample papers and previous year's question papers as possible. Also, solve chapter-wise board questions to gain a strong command over each chapter.
- Focus on Practical Subjects: For subjects with practical components, ensure you spend sufficient time in the lab and understand the experiments thoroughly.
- Revise Regularly: Keep revising the concepts regularly, and make sure to cover all the important topics at least two months before the exams.


